Abstract
Introduction
Ibrutinib is a first-in-class, oral, covalent inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase that is approved in many countries for the treatment of treatment-naïve (TN) and relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). In the phase 3 RESONATE-2™ trial (NCT01722487; Burger JA, et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2425-2437), ibrutinib significantly improved overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) over chlorambucil in TN patients. However, several alternative treatments are widely used in the real-world (RW) clinical setting, for which head-to-head clinical studies and comparative effectiveness data are limited. The aim of this study was to estimate the relative treatment effect of ibrutinib versus RW treatment regimens in daily clinical practice in TN CLL patients, by adjusted comparison of patient-level data (PLD) from the RESONATE-2™ trial and RW outcomes from two different countries.
Methods
The two RW data sources used were the Lyon-Sud database, which holds medical records for CLL patients diagnosed between 1990 and 2016 from the Centre Hospitalier Lyon-Sud, France, and the Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Registry (CLLEAR), which holds medical records for CLL patients diagnosed between 1994 and 2016 from 7 academic centers across the Czech Republic. Patient-cohorts of TN CLL patients (majority treated post-2005) were selected using the RESONATE-2™ inclusion criteria, excluding patients aged < 65 years and those with del17p positive status.
PFS and OS outcomes were compared between ibrutinib and RW (physician's choice) treatment using PLD from both the ibrutinib arm of RESONATE-2™ and the pooled RW databases (excluding any RW ibrutinib patients). To account for differences in patient populations between the clinical trial and RW settings (due to lack of randomization), a multivariate Cox proportional hazards model was fitted on the PLD to estimate adjusted hazard ratios (HR) for the treatment effect of ibrutinib versus RW treatment. Age, sex, del11q status, and disease stage (based on Binet/Rai systems) were included as covariates. The multivariate model enabled prediction of PFS and OS for the RW cohort, assuming that they would have been treated with ibrutinib.
Results
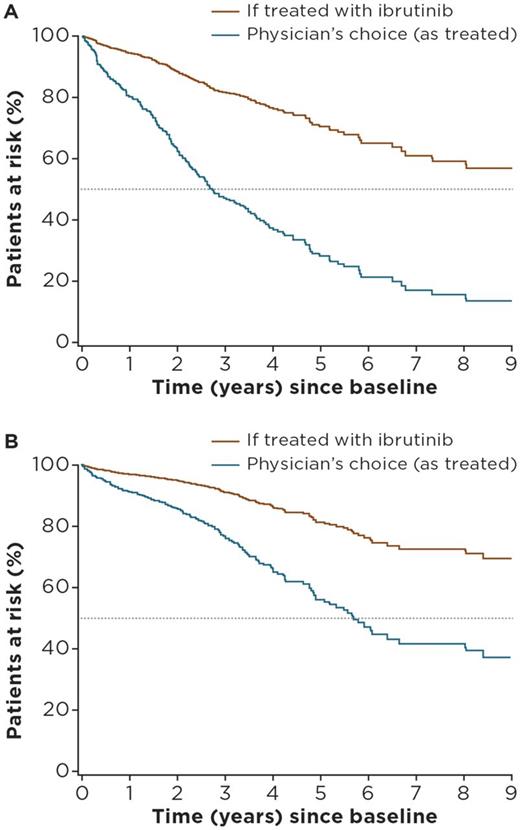
For the pooled TN cohorts of Lyon-Sud and CLLEAR (n = 544), median age was 72 years, 62% of patients were male, and median follow-up was 28.1 months (Lyon-Sud: 64.9 months; CLLEAR: 20.2 months). For the ibrutinib arm of RESONATE-2™ (n = 136), median age was 73 years, 65% of patients were male, and median follow-up was 28.1 months. The most commonly used treatment regimens for TN CLL in the RW cohorts were fludarabine + cyclophosphamide + rituximab (n = 137 [25.5%]), bendamustine + rituximab (n = 98 [18%]), chlorambucil alone (n = 48 [8.8%]), chlorambucil + rituximab (n = 56 [10.3%]), and other rituximab-containing regimens (n = 146 [26.8%]). Multivariate analysis showed older age, male sex, del11q positive status, and advanced disease stage were independent risk factors for PFS and OS. Adjusted HRs for ibrutinib versus physician's choice (all regimens) of therapy were 0.26 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.15-0.45) for PFS and 0.33 (95% CI: 0.16-0.70) for OS. Adjusted HRs for ibrutinib versus the most commonly used regimens ranged between 0.38 (95% CI: 0.18-0.78) (bendamustine + rituximab) and 0.14 (95% CI: 0.07-0.27) (chlorambucil) for PFS, and between 0.60 (95% CI: 0.23-1.56) (chlorambucil + rituximab) and 0.22 (95% CI: 0.10-0.49) (other rituximab-combinations) for OS . Estimates of treatment effect were generally consistent between both countries and remained similar when restricting analysis to patients diagnosed after 2000. Figures 1A and B show PFS and OS estimated survival curves for the pooled RW-cohort (if treated with ibrutinib) versus observed outcomes.
Conclusions
Adjusted comparisons of clinical trial and RW PLD suggest that ibrutinib significantly improves survival outcomes versus commonly used regimens in TN CLL (estimated 3.8-fold improvement in PFS and 3-fold improvement in OS). The findings improve our understanding of the standard of care and inform physicians of the comparative effectiveness of ibrutinib in the RW.
Figure 1: Predicted (A) PFS and (B) OS for TN CLL patients from the pooled RW cohorts if treated with ibrutinib versus physician's choice regimen
Salles: Celgene: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board; Gilead: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board; Janssen: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board; Amgen: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board; Kite: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board; Merck: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board; Morphosys: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board; Roche: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board, Research Funding; Servier: Consultancy, Other: Advisory board. Smolej: Roche/Genentech, Janssen, Gilead, and AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel grants. Bachy: Amgen: Honoraria; Sandoz: Consultancy, Honoraria; Mundipharma: Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Besson: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV: Other: employee of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. Hermans: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV: Other: employee of QuintilesIMS, which is the vendor paid by Janssen Pharmaceutica NV to perform the extracting/cleaning/harmonization of the data. Healy: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV: Other: employee of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. Garside: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV: Other: employee of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. Iraqi: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV: Other: employee of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. Diels: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV: Other: employee and equity owner of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. MacDougall: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV: Other: employee of QuintilesIMS, which is the vendor paid by Janssen Pharmaceutica NV to perform the extracting/cleaning/harmonization of the data. Pick-Lauer: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV: Other: employee of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. Spacek: AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, and Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria. Lysak: Gilead, Janssen, and Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria. Doubek: AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead, Janssen, and Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal